Started By
Message
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Posted on 7/28/22 at 3:20 pm
Posted on 7/28/22 at 3:20 pm
This was pretty cool.
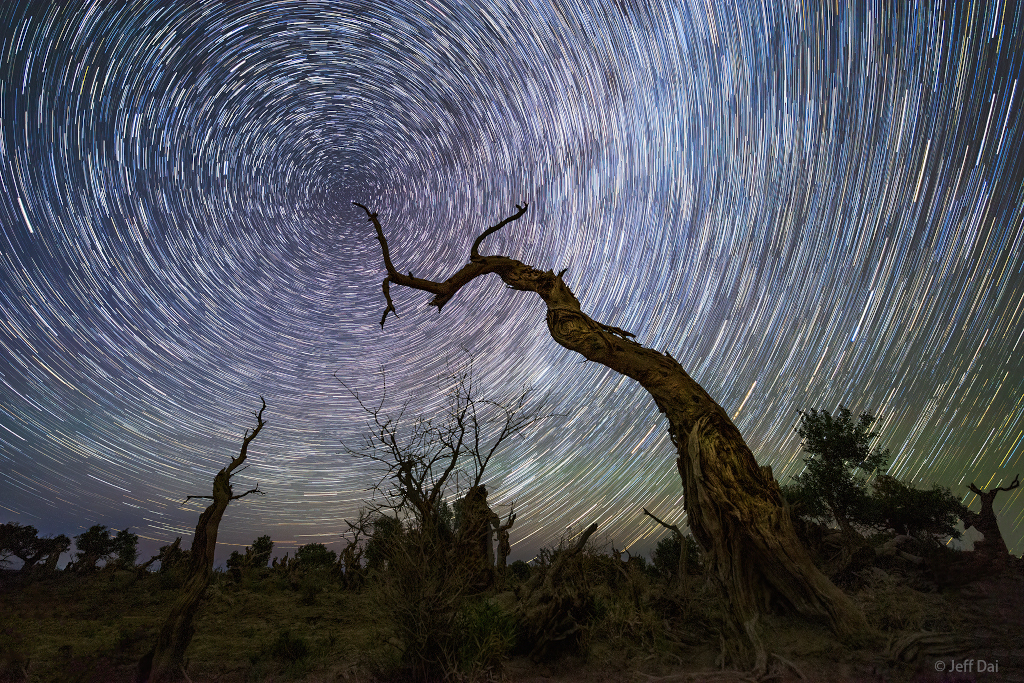

North Celestial Tree
Image Credit & Copyright: Jeff Dai (TWAN)
Explanation: An ancient tree seems to reach out and touch Earth's North Celestial Pole in this well-planned night skyscape. Consecutive exposures for the timelapse composition were recorded with a camera fixed to a tripod in the Yiwu Desert Poplar Forests in northwest Xinjiang, China. The graceful star trail arcs reflect Earth's daily rotation around its axis. By extension, the axis of rotation leads to the center of the concentric arcs in the night sky. Known as the North Star, bright star Polaris is a friend to northern hemisphere night sky photographers and celestial navigators alike. That's because Polaris lies very close to the North Celestial Pole on the sky.
APOTD

North Celestial Tree
Image Credit & Copyright: Jeff Dai (TWAN)
Explanation: An ancient tree seems to reach out and touch Earth's North Celestial Pole in this well-planned night skyscape. Consecutive exposures for the timelapse composition were recorded with a camera fixed to a tripod in the Yiwu Desert Poplar Forests in northwest Xinjiang, China. The graceful star trail arcs reflect Earth's daily rotation around its axis. By extension, the axis of rotation leads to the center of the concentric arcs in the night sky. Known as the North Star, bright star Polaris is a friend to northern hemisphere night sky photographers and celestial navigators alike. That's because Polaris lies very close to the North Celestial Pole on the sky.
APOTD
Posted on 8/10/22 at 6:09 am to Trumansfangs
quote:
The title of North Star passes to different stars over time. Earth's axis of rotation wobbles over the course of about 26,000 years, the way a spinning top also wobbles as it spins. This causes the celestial pole to wander in a slow circle over the eons, sweeping past different stars.
Sometimes there's no bright star near the celestial pole, as is the case in the Southern Hemisphere at present. Observers there can use other clever ways to find due south, including using the stars of the Southern Cross constellation to point the way.
About 14,000 years ago, the celestial pole in the north pointed toward the bright star Vega, and as it sweeps out its slow circle, it will again point to Vega in about 12,000 years.
Back to top

 1
1